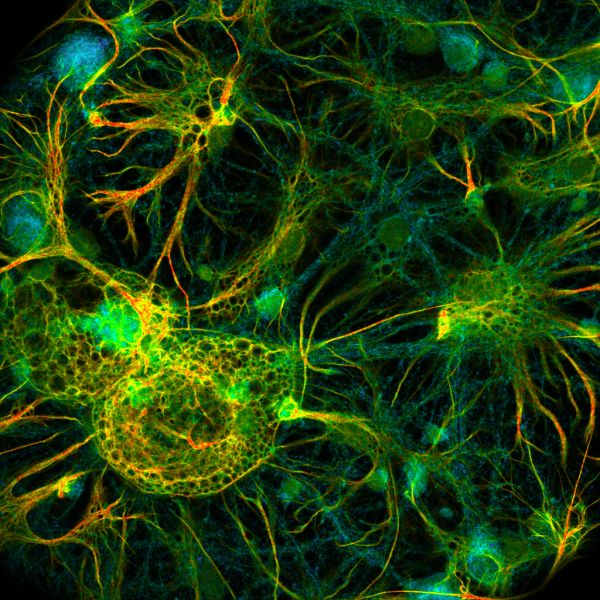
44 fluorescent labels and light microscopy
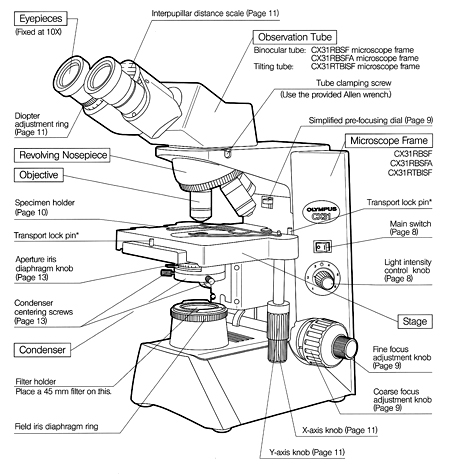
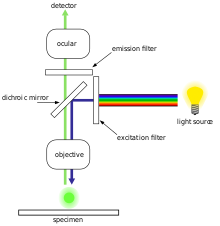
How to Prepare Your Specimen for Immunofluorescence Microscopy Jan 10, 2022 · Immunofluorescence (IF) is a powerful method for visualizing intracellular processes, conditions and structures. IF preparations can be analyzed by various microscopy techniques (e.g. CLSM, Epifluorescence, TIRF, GSDIM), depending on the application or the researcher’s interest.Meanwhile, IF has become indispensable for a large number of research … ZEISS LSM 980 with Airyscan 2 NIR fluorescent labels are less phototoxic for living samples due to the longer wavelength. This allows you to investigate living samples for longer periods of time while limiting the influence of light. Additionally, light of longer wavelength ranges is less scattered by the sample tissue, increasing penetration depth.
Two-photon excitation microscopy - Wikipedia Two-photon excitation microscopy (TPEF or 2PEF) is a fluorescence imaging technique that allows imaging of living tissue up to about one millimeter in thickness, with 0.64 μm lateral and 3.35 μm axial spatial resolution. Unlike traditional fluorescence microscopy, in which the excitation wavelength is shorter than the emission wavelength, two-photon excitation requires …
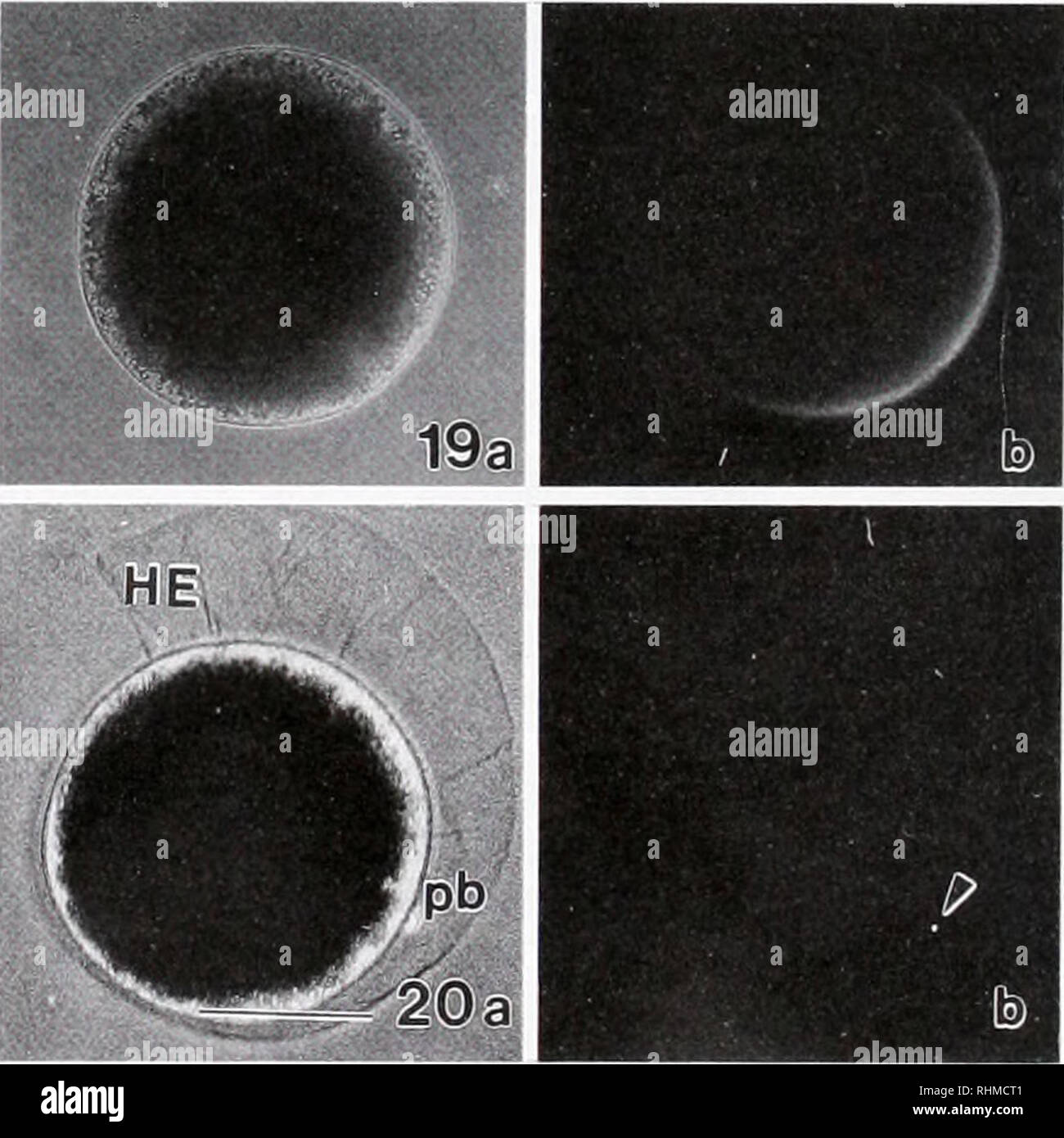
Fluorescent labels and light microscopy
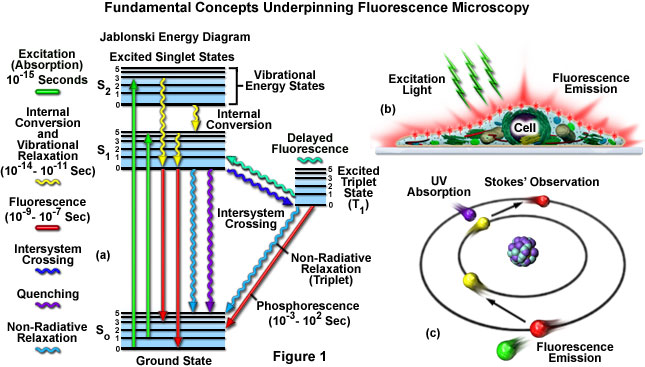
Fluorescence - Wikipedia Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation.It is a form of luminescence.In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation.A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the … Super-resolution microscopy - Wikipedia Super-resolution microscopy is a series of techniques in optical microscopy that allow such images to have resolutions higher than those imposed by the diffraction limit, which is due to the diffraction of light. Super-resolution imaging techniques rely on the near-field (photon-tunneling microscopy as well as those that utilize the Pendry Superlens and near field scanning optical … Förster resonance energy transfer - Wikipedia Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), resonance energy transfer (RET) or electronic energy transfer (EET) is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules (chromophores). A donor chromophore, initially in its electronic excited state, may transfer energy to an acceptor chromophore through nonradiative dipole–dipole coupling.
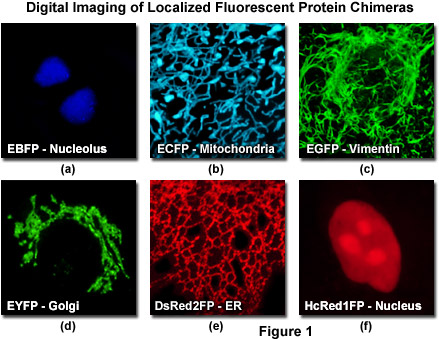
Fluorescent labels and light microscopy. Expansion microscopy: principles and uses in biological research Dec 20, 2018 · After gelation, digestion, and expansion, the fluorescence of the antibody labels or fluorescent proteins is largely retained for many genetically encoded fluorophore and small-molecule dyes (Fig ... (PDF) Introduction to Microscopy - ResearchGate Nov 08, 2017 · 1. Microscopy with light and electrons 2. Electron/specimen interactions: processes and detectors 3. The electron microscope family 4. Specimen preparation for electron microscopy 5. cellSens | Imaging Software | Olympus LS - Life Science Olympus cellSens software provides an intuitive imaging experience and seamless workflow for evolving research needs. Find out more. Introduction to Fluorescent Proteins | Nikon’s MicroscopyU The brightness and fluorescence emission spectrum of enhanced yellow fluorescent protein combine to make this probe an excellent candidate for multicolor imaging experiments in fluorescence microscopy. Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein is also useful for energy transfer experiments when paired with enhanced cyan fluorescent protein (ECFP) or ...
Förster resonance energy transfer - Wikipedia Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), resonance energy transfer (RET) or electronic energy transfer (EET) is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules (chromophores). A donor chromophore, initially in its electronic excited state, may transfer energy to an acceptor chromophore through nonradiative dipole–dipole coupling. Super-resolution microscopy - Wikipedia Super-resolution microscopy is a series of techniques in optical microscopy that allow such images to have resolutions higher than those imposed by the diffraction limit, which is due to the diffraction of light. Super-resolution imaging techniques rely on the near-field (photon-tunneling microscopy as well as those that utilize the Pendry Superlens and near field scanning optical … Fluorescence - Wikipedia Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation.It is a form of luminescence.In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation.A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the …
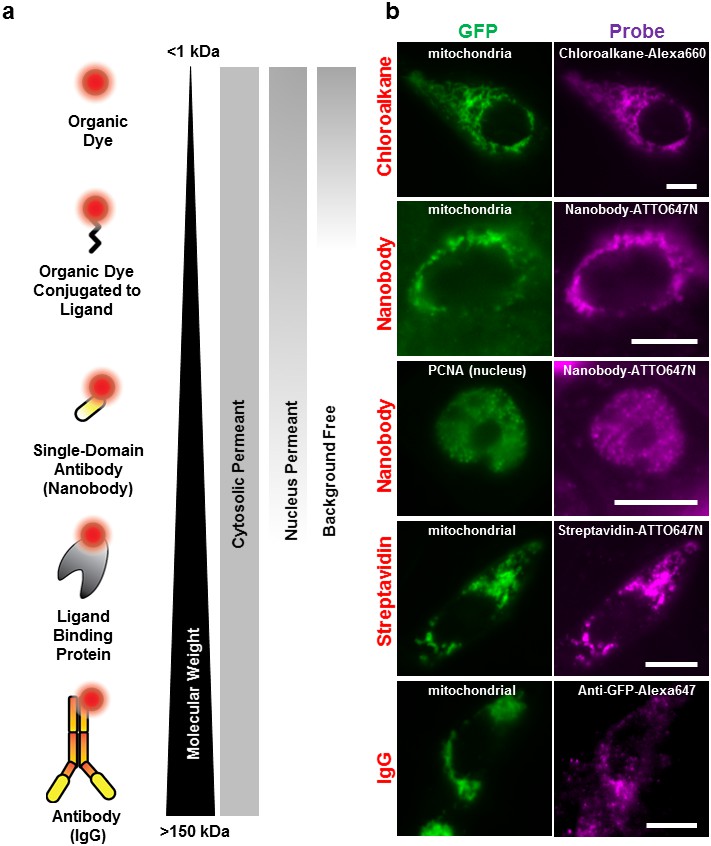
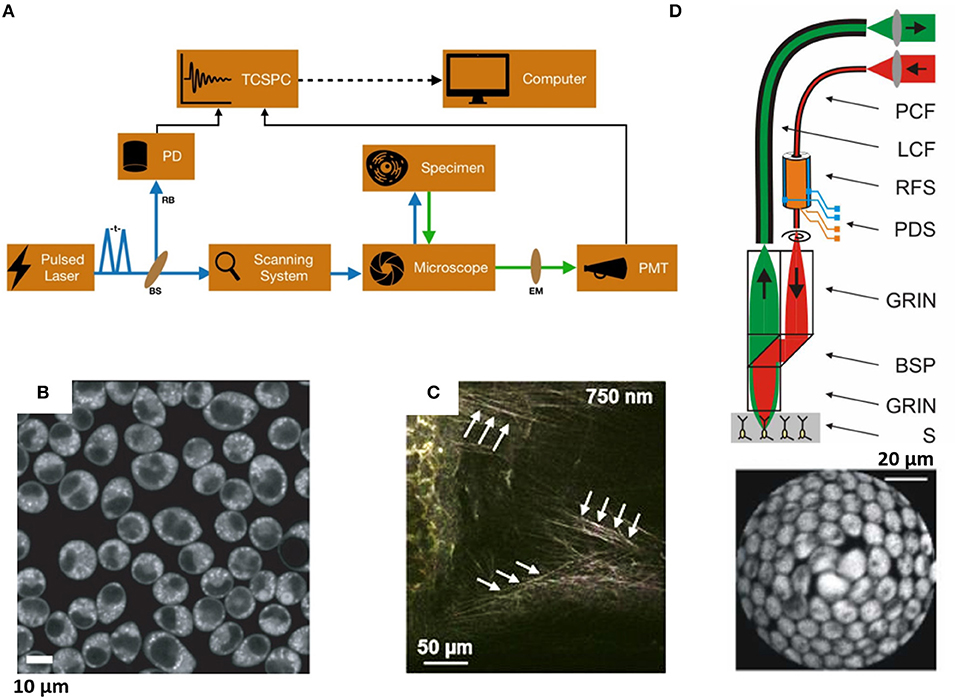



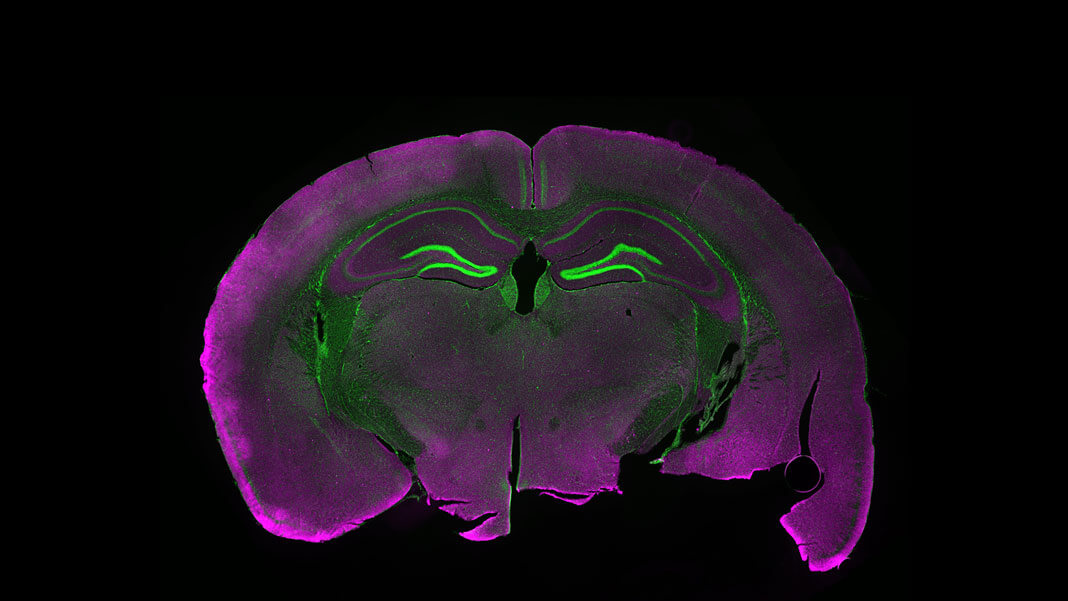

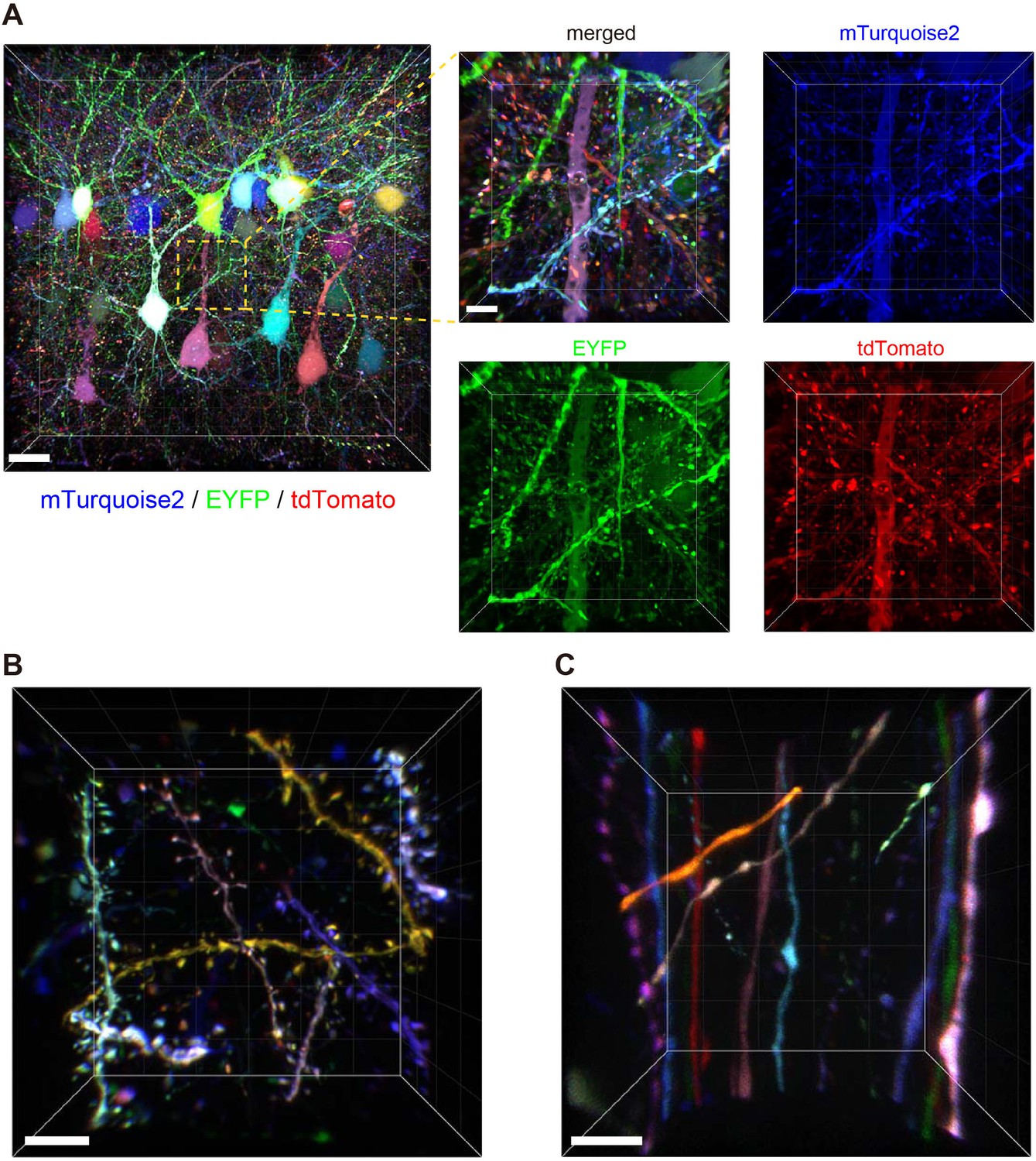
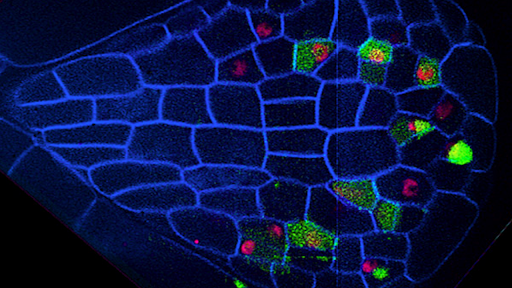
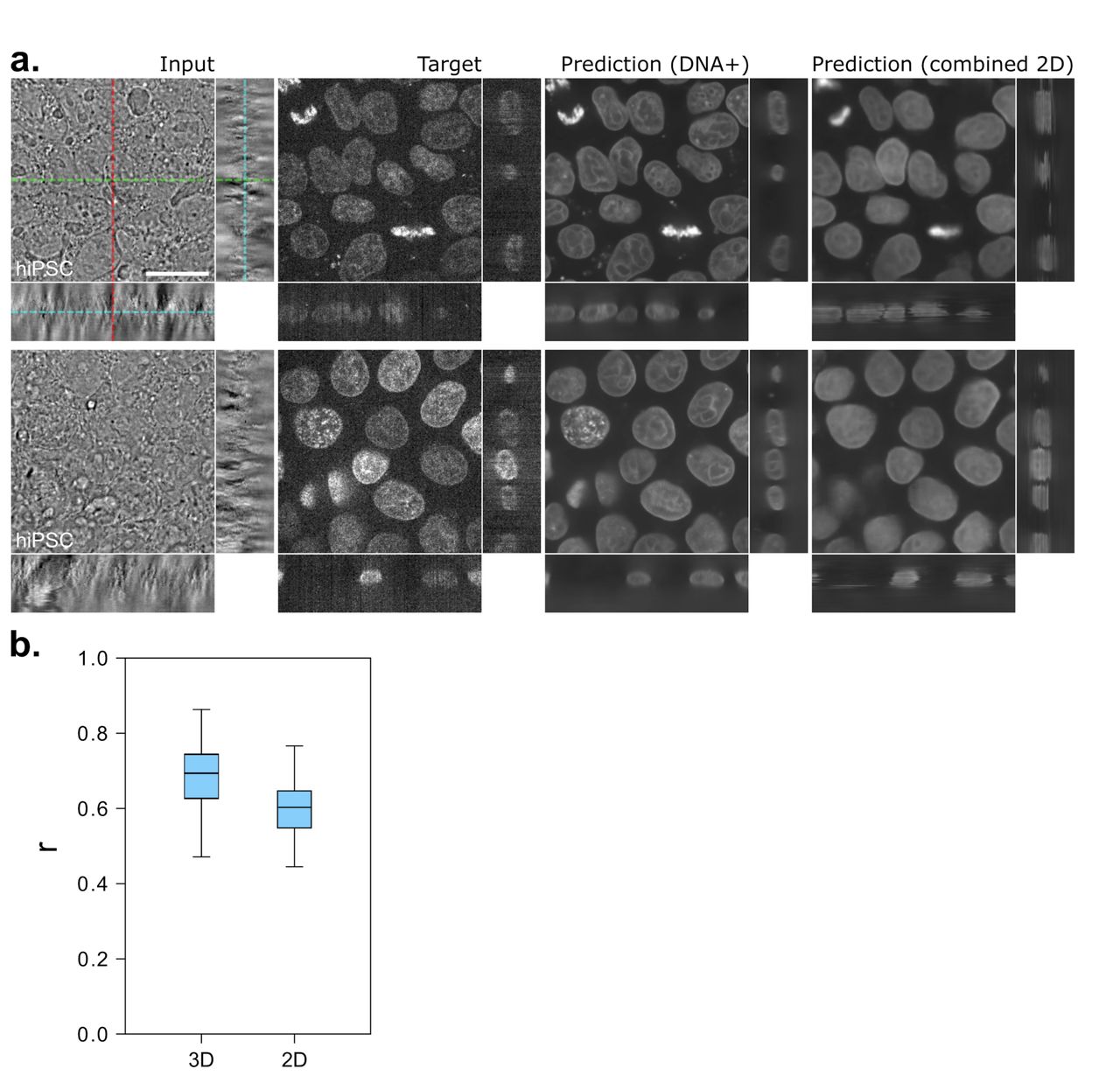

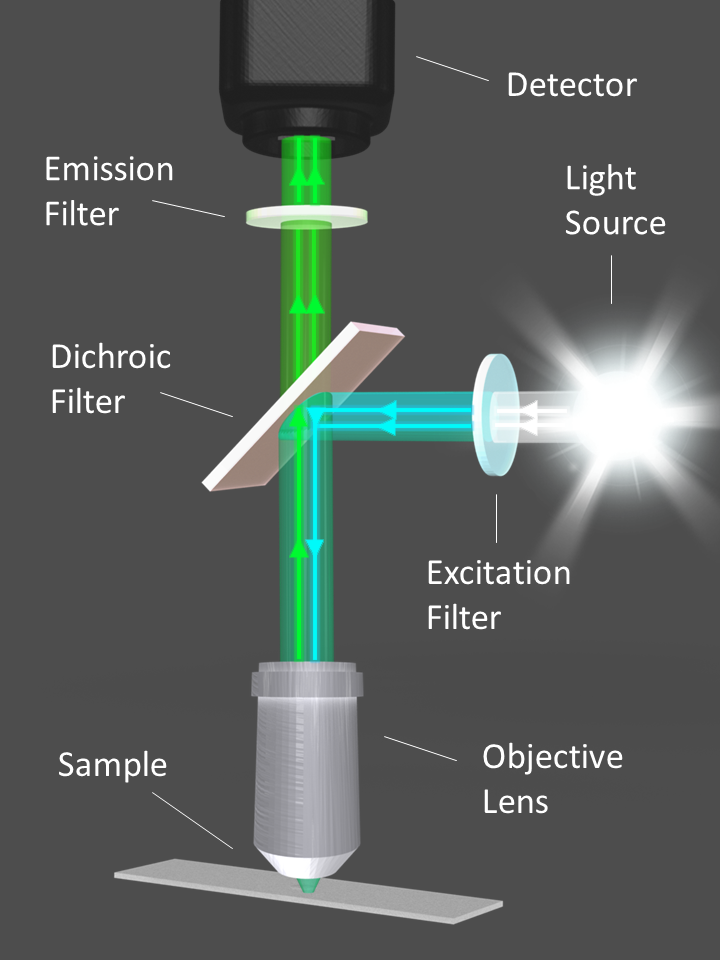



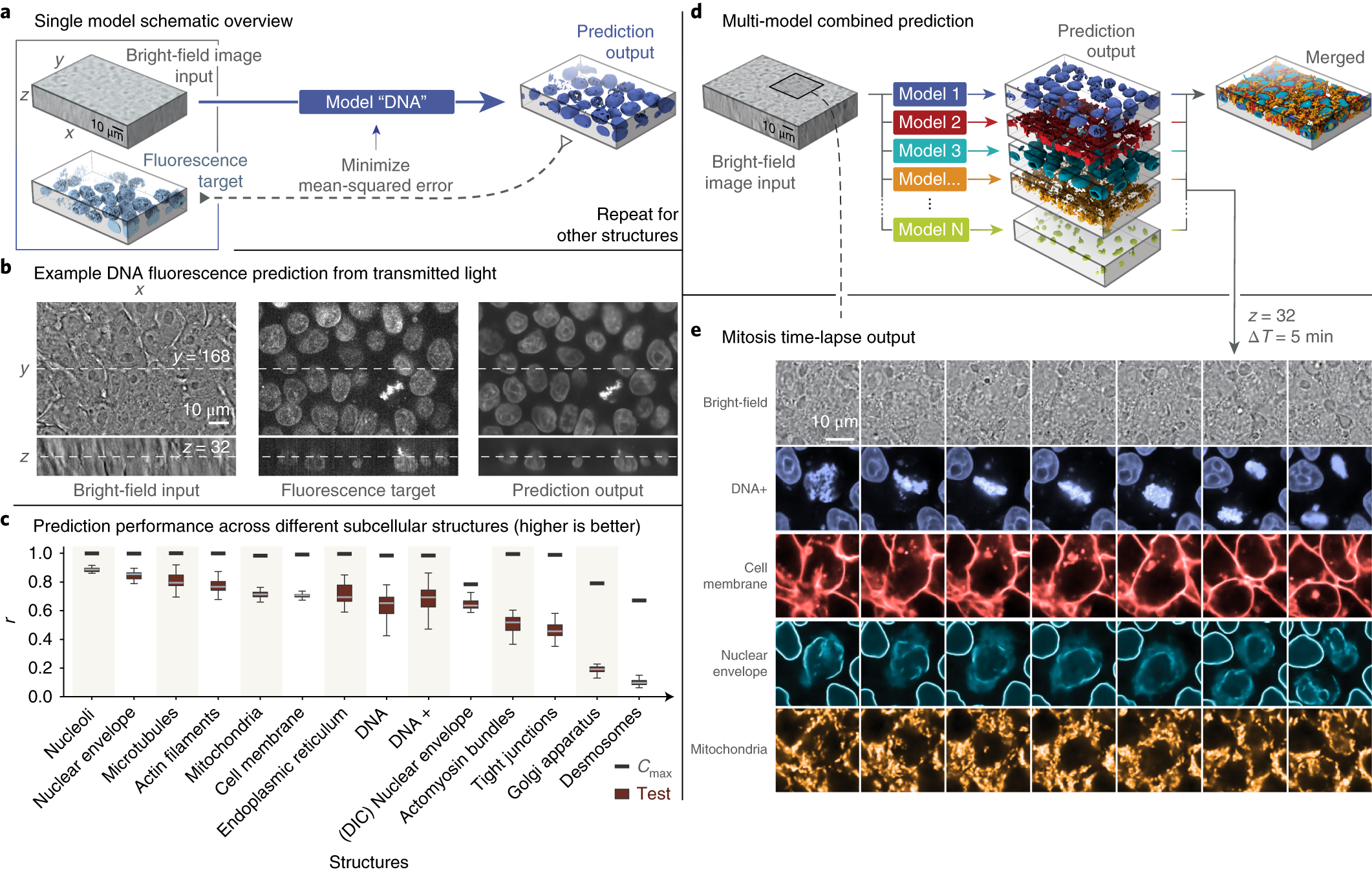

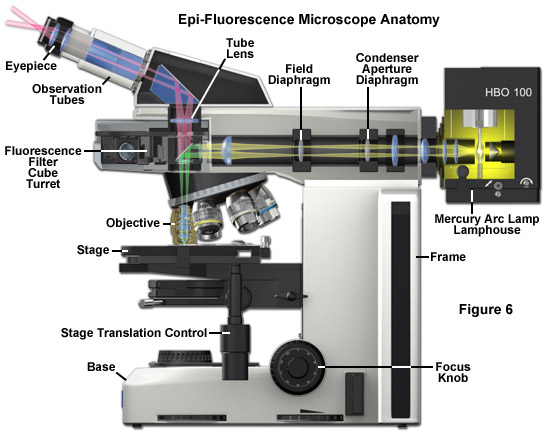

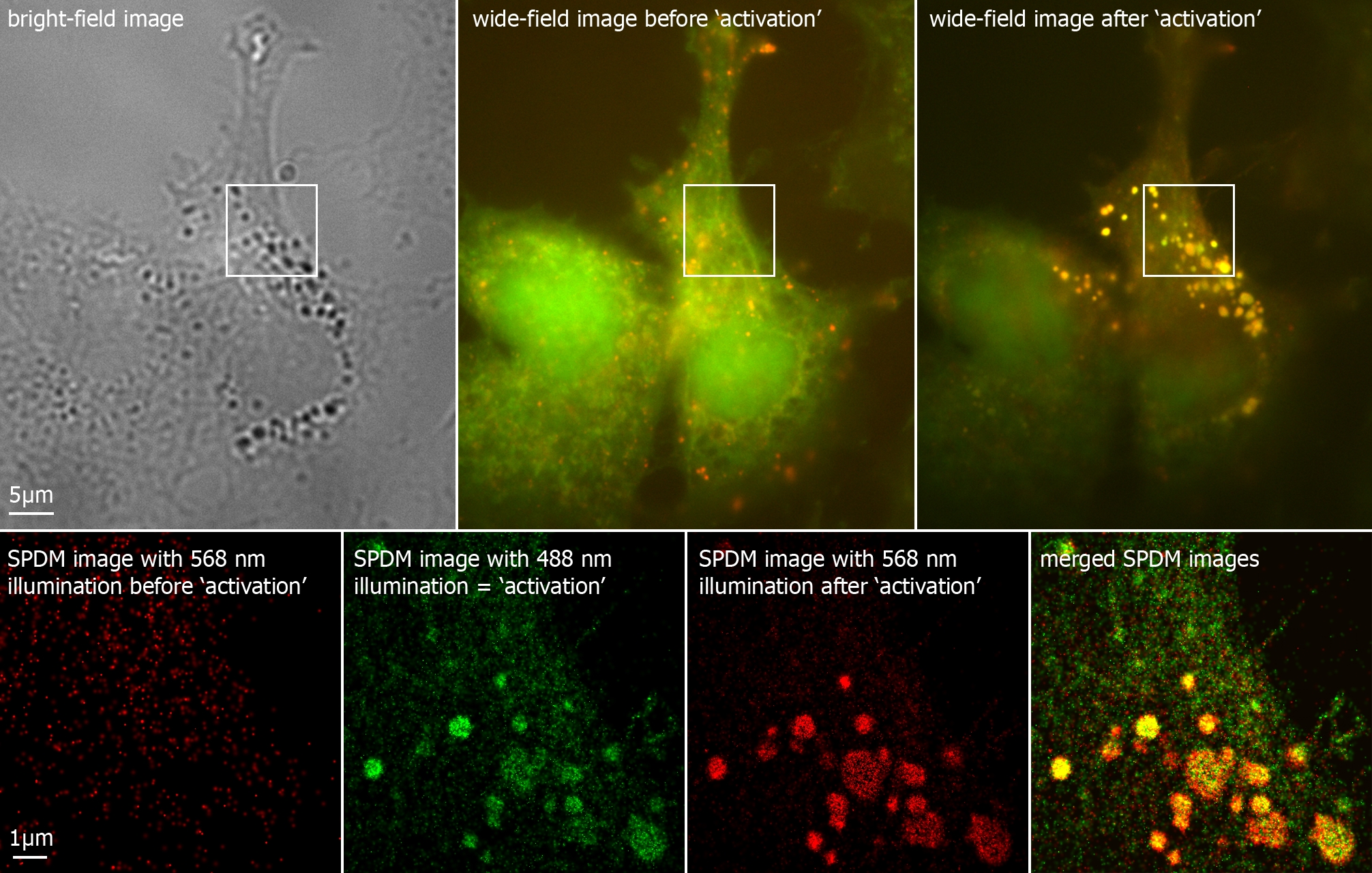





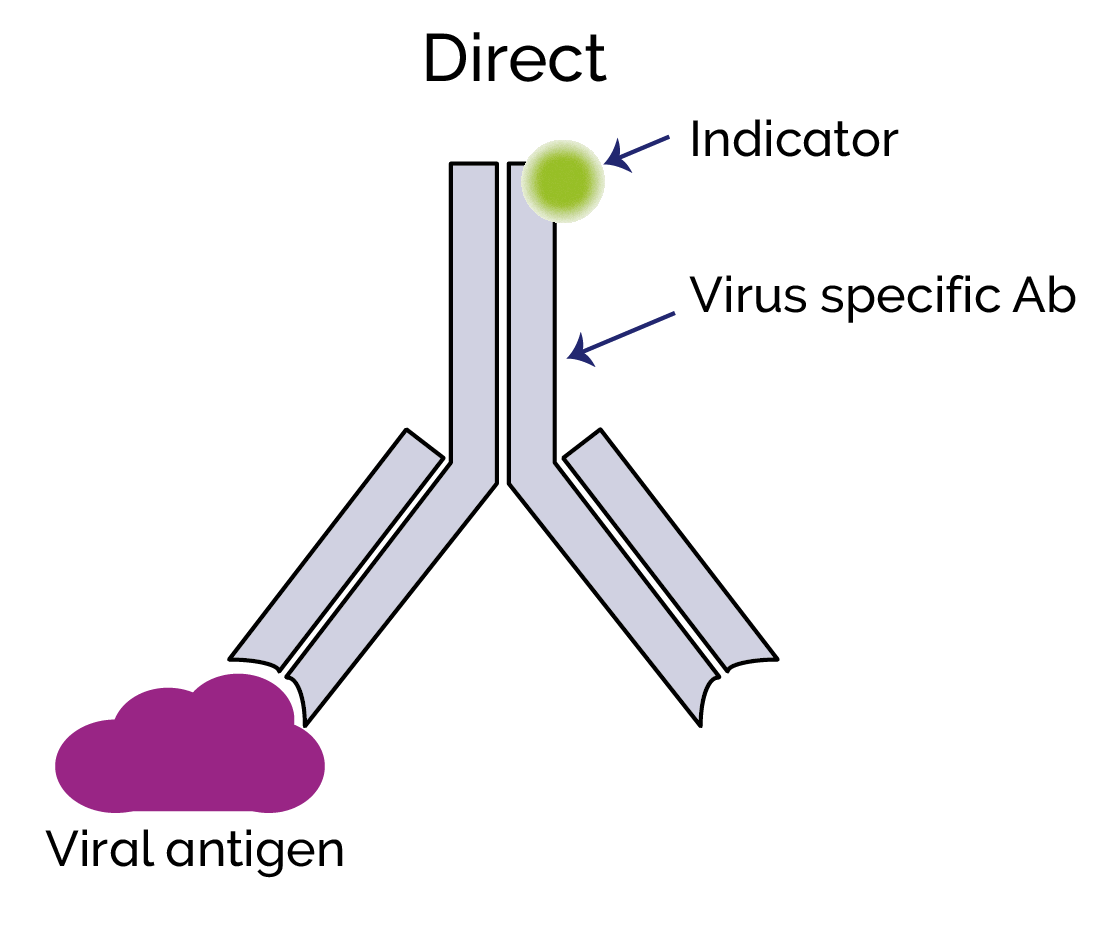
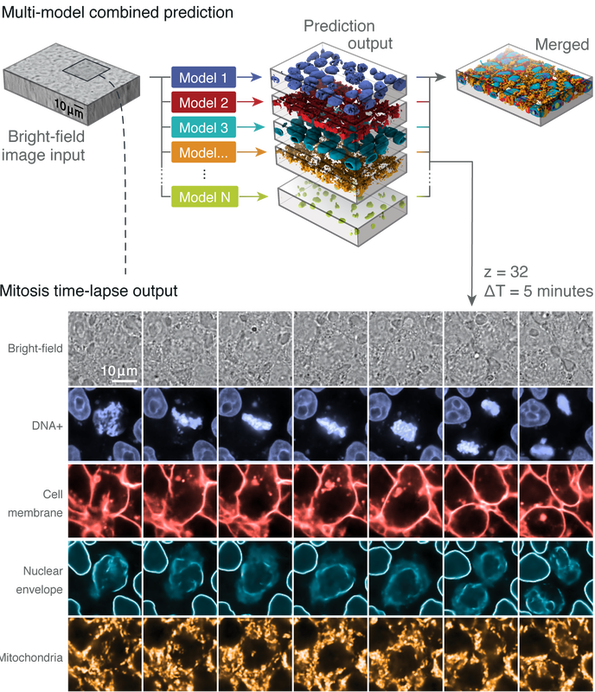
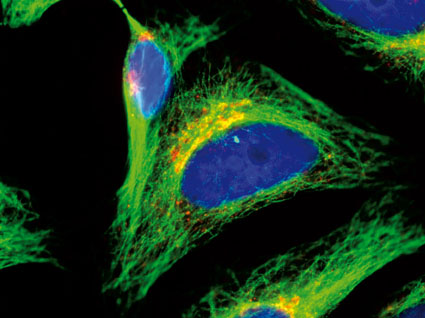

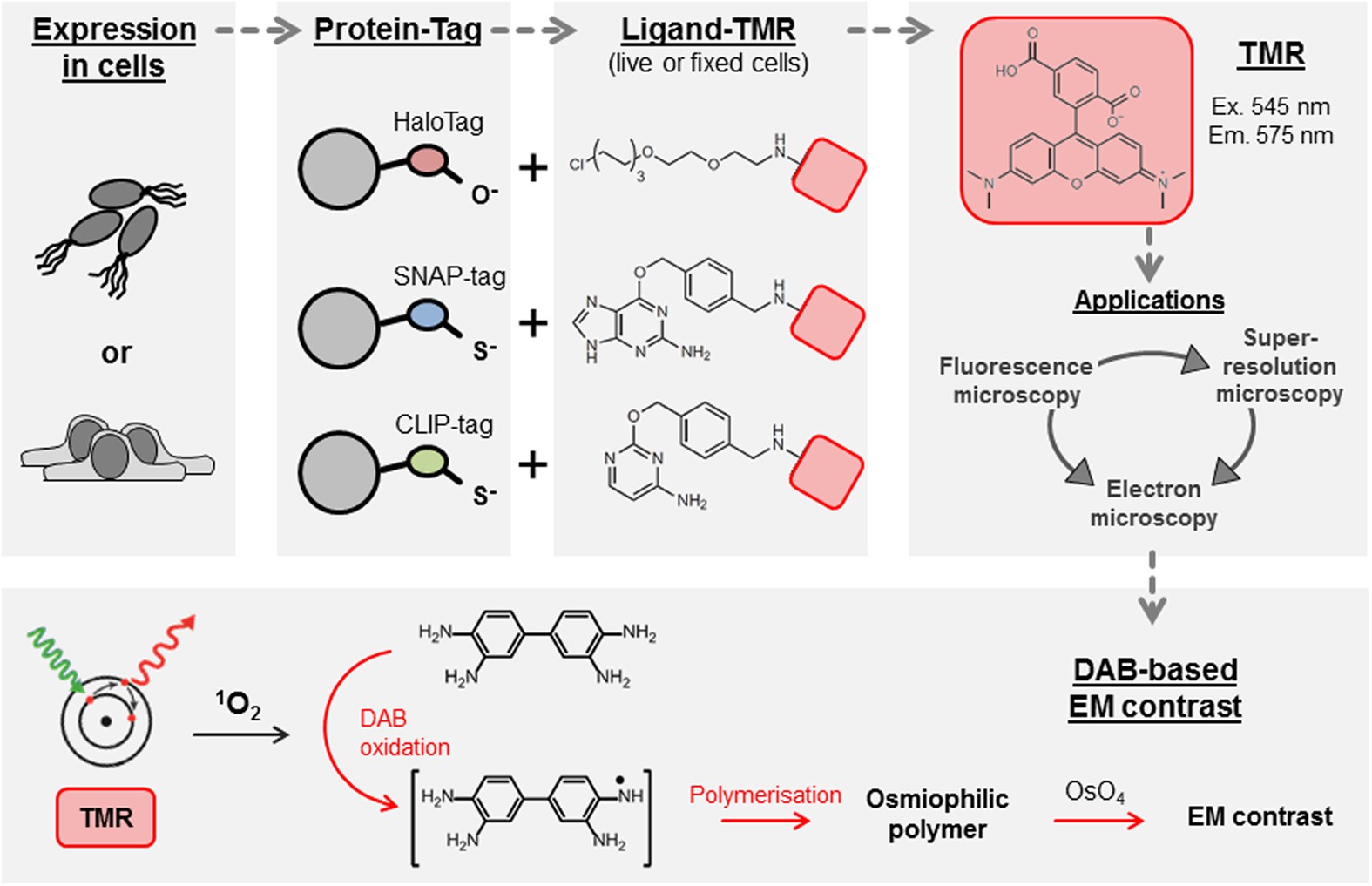
Post a Comment for "44 fluorescent labels and light microscopy"